How do most computer languages evaluate and make simple decisions? Mostly through the use of the conditional 'If' statement. Whats more Ruby is no different though a lot might argue including myself a hell of a lot easier. So lets take a look at this statement in action shall we?
irb(main):001:0> age = 50
=> 50
irb(main):002:0> if age < 50
irb(main):003:1> puts('still a few years on the clock yet')
irb(main):004:1> else
irb(main):005:1* puts('too bad')
irb(main):006:1> end
too bad
First off we set assigned 50 to the age. Then we started with the conditional 'if' to evaluate the age where we used an operator < which means less than. So we said if age was less than 50 print the first message or if not print the second message.
And that's a simple way to use the conditional 'if' operator in Ruby.
Beginners Ruby Programming Books Resource
Learn To Program In Bite Sized Chunks Using Ruby & Python
Monday, 3 March 2014
How To Assign Basic Values To Variable In Ruby
Assigning Values To Variables in Ruby is a pretty easy thing to do. Once you learn it there's no end to the fun you can have with this programming language.
Here are a couple of examples as how you can manipulate variables and their values in Ruby.
irb(main):001:0> x = 50
=> 50
irb(main):002:0> y = 100
=> 100
irb(main):003:0> puts x + y
150
Firstly we assigned numbers to the variables x and y. Then we used the 'puts' method to output the combined value of x + y to arrive at our total of 150! Simples!
Here are a couple of examples as how you can manipulate variables and their values in Ruby.
irb(main):001:0> x = 50
=> 50
irb(main):002:0> y = 100
=> 100
irb(main):003:0> puts x + y
150
Firstly we assigned numbers to the variables x and y. Then we used the 'puts' method to output the combined value of x + y to arrive at our total of 150! Simples!
Friday, 14 February 2014
Basic Variables In Ruby
Basic Variables
Variables are very important in Ruby programming, but the good news is that you don;t have to be a rocket scientist to be able to understand them because they're really quite straightforward. For our first example we'll take a look at assigning a letter to a number.
irb(main):001:0> x = 20
=> 20
irb(main):002:0>
Here we have assigned the letter x to equal or represent 20. Now x = 20 and we can prove this by asking Ruby to print out the value of x.
irb(main):002:0> puts x
20
=> nil
irb(main):003:0>
You can now play around with your variables by adding or multiplying with them like so.
irb(main):003:0> x + 5
=> 25
We can see here that the value of x is now 25 because we've added a + sign with a 5.
Later on we'll take a closer look at these operators * + - etcwhen we delve more into Ruby variables.
Variables are very important in Ruby programming, but the good news is that you don;t have to be a rocket scientist to be able to understand them because they're really quite straightforward. For our first example we'll take a look at assigning a letter to a number.
irb(main):001:0> x = 20
=> 20
irb(main):002:0>
Here we have assigned the letter x to equal or represent 20. Now x = 20 and we can prove this by asking Ruby to print out the value of x.
irb(main):002:0> puts x
20
=> nil
irb(main):003:0>
You can now play around with your variables by adding or multiplying with them like so.
irb(main):003:0> x + 5
=> 25
We can see here that the value of x is now 25 because we've added a + sign with a 5.
Later on we'll take a closer look at these operators * + - etcwhen we delve more into Ruby variables.
Wednesday, 12 February 2014
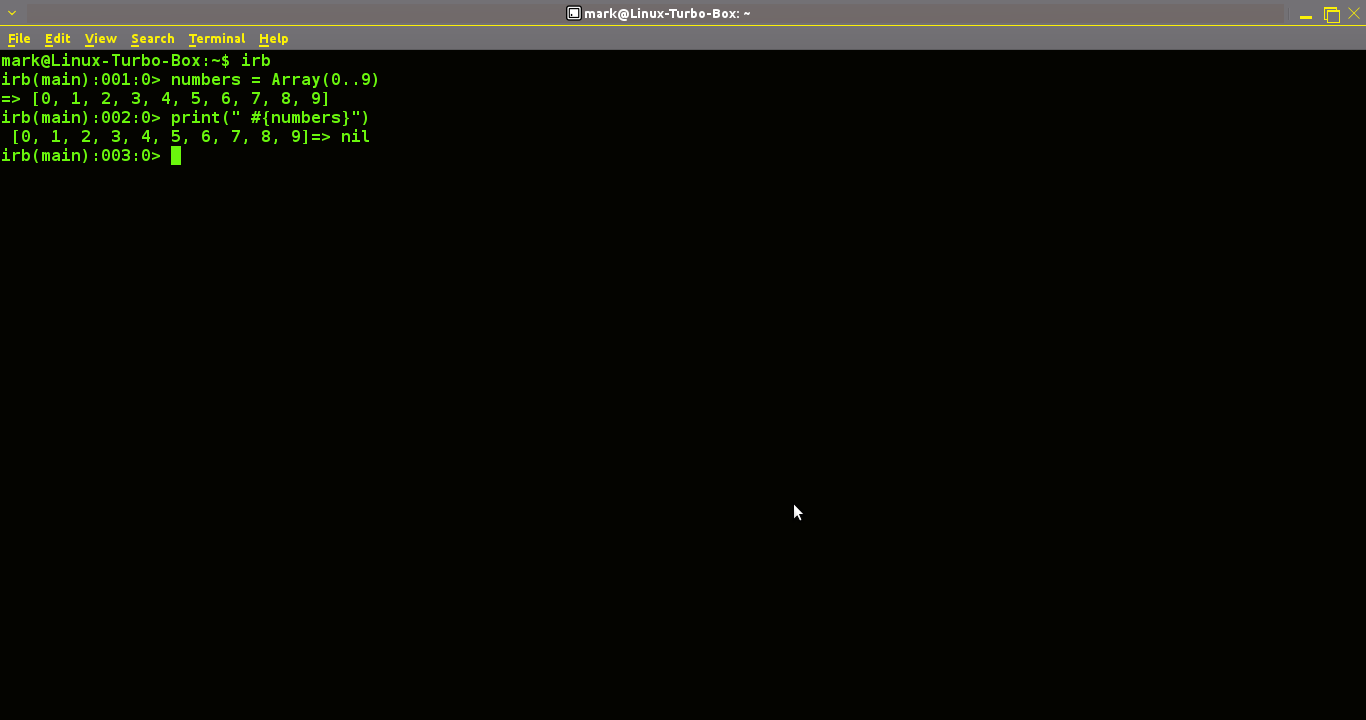
Creating An Array Of Numbers In Ruby
Our next bite sized chunk of Ruby coding will focus on how to create a simple array of numbers. Okay, head on over to your favourite terminal, fire it up and input the following.
irb(main):004:0> numbers = Array(0..9)
Here we've set the numbers in our array from zero to nine. Then we hit enter and the output is this.
=> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Next, enter the following code:
print(" #{numbers} ")
And hey voila Ruby out puts your array of numbers.
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] => nil
And that's your basic Ruby array of numbers.
How To Add Elements To A Ruby Array Using (.push)
In the last post we examined how to delete elements from the Ruby array using the .pop method. In this short code snippet we're going to take a look at how to use Ruby to add extra elements to the array via the .push method. As always head on over to your shell if you're using Linux and go into irb. Then type out the following code.
new_array = ['Britain','Thailand','USA']
=> ["Britain", "Thailand", "USA"]
And there you have our array of countries like so. Next type in this.
new_array.push('Italy')
Here we see the .push method along with the latest country we want to add to our Ruby array list.
=> ["Britain", "Thailand", "USA", "Italy"]
Once you hit enter your newly updated array is returned with an addition to it. It's worth mentioning here that we can also push elements into the array via this method <<.
irb(main):003:0> new_array << 'germany'
And the returned output is:
=> ["Britain", "Thailand", "USA", "Italy", "germany"]
Germany being added to our new Ruby array.
Saturday, 8 February 2014
Reversing The Elements In A Ruby Array
So you've got your Ruby array and you want to reverse the elements in it! With the Ruby programming this task is easily accomplished with the following code. First off go and create an array in irb something like this.
my_array = ['mark','dave',1,2,3,'x']
Next we will use the reverse command on this array like so:
puts my_array.reverse
This will print the following output to your screen.
x
3
2
1
dave
mark
Notice here that this output has been printed out like a list. The reason for this is that we used 'puts' to output it. If you want to see the output of your array printed on the same line, simply substitute the 'puts' command for the Ruby 'print' command like so.
print my_array.reverse
["x", 3, 2, 1, "dave", "mark"]
And hey voila Ruby will print the output on the same line!
Tuesday, 4 February 2014
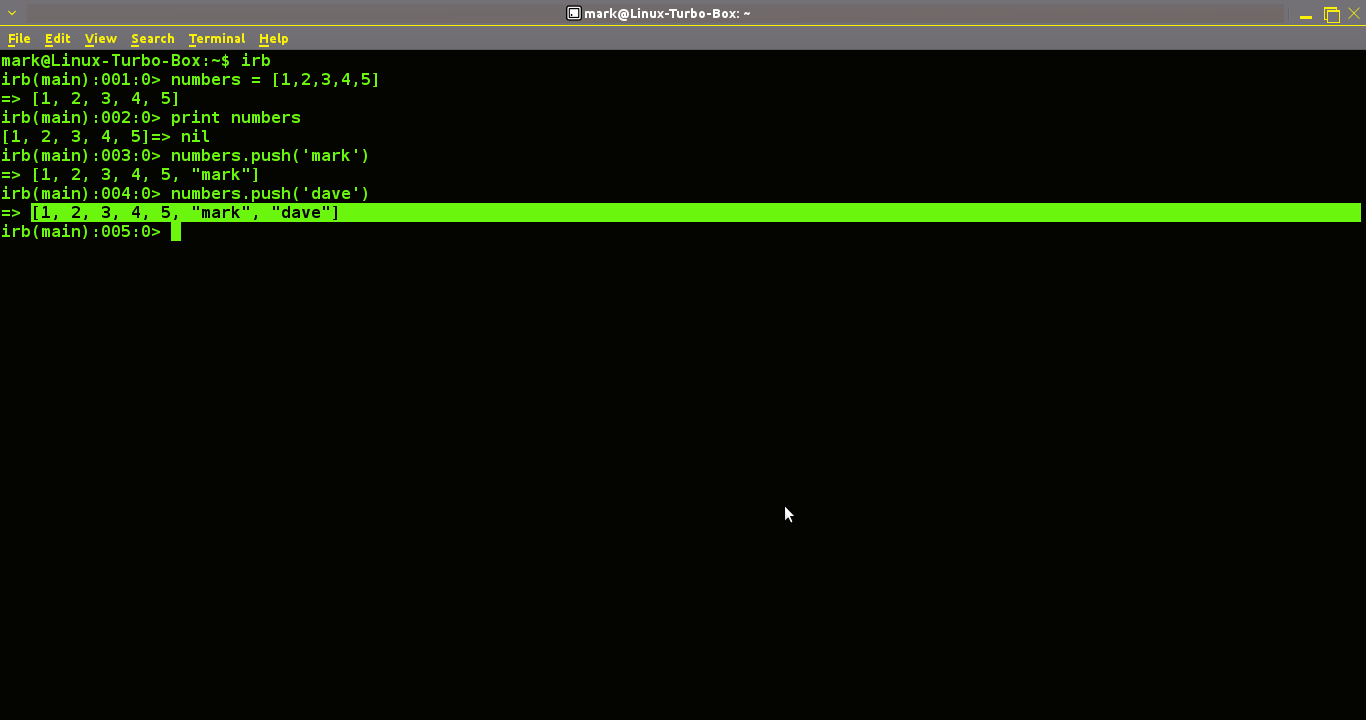
How To Add Extra Elements Into A Ruby Array
Adding Additional Things Into A Ruby Array
Once you've got your array in Ruby you might want to add extra elements to it. With ruby this is easy.
Create a new array, this time I've created an array of numbers. The keener eyed reader out there will have spotted that you don't need quotations around the numbers - but they do have to be divided by commas. So go ahead and create a new array:
numbers = [1,2,3,4,5]
Now we simple want to add extra elements onto the end of this array. We accomplish this by a line of code like this:
numbers.push('mark')
We then hit enter and here is the output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "mark"]
There you can see 'Mark' has been added onto the end of the array.
numbers.push('dave')
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "mark", "dave"]
And finally we're able to add more and more elements as we want. And that's how to add elements onto an array in Ruby.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)